- Search
Most viewed
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most viewed
"Most viewed" articles are updated on a quarterly basis. The following are the most frequently accessed articles from Annals of Coloproctology in the preceding months.
- Video clip
- Cranial-first approach for laparoscopic extended right hemicolectomy (1,224 times)
- Kyong-Min Kang, Heung-Kwon Oh, Hong-Min Ahn, Tae-Gyun Lee, Hye-Rim Shin, Mi-Jeong Choi, Duck-Woo Kim, Sung-Bum Kang
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(3):282-284. Published online June 19, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF  Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material
- Local plus oral antibiotics and strict avoidance of constipation is effective and helps prevents surgery in most cases of anal fissure (7,773 times)
- Pankaj Garg, Vipul D. Yagnik, Kaushik Bhattacharya
- Ann Coloproctol. 2023;39(2):188-189. Published online November 29, 2022
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Colorectal cancer
- Public effect of the 2022 Colorectal Cancer Awareness Campaign delivered through a metaverse platform (7,300 times)
- Tae-Gyun Lee, Gil-Hyeon Song, Hong-min Ahn, Heung-Kwon Oh, Moonkyoung Byun, Eon Chul Han, Sohyun Kim, Chang Woo Kim, Hye Jin Kim, Samin Hong, Kee-Ho Song, Chan Wook Kim, Yong Beom Cho, on behalf of the Public Relations Committee of the Korean Society of Coloproctology (KSCP)
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(2):145-153. Published online April 28, 2023
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Anorectal benign disease
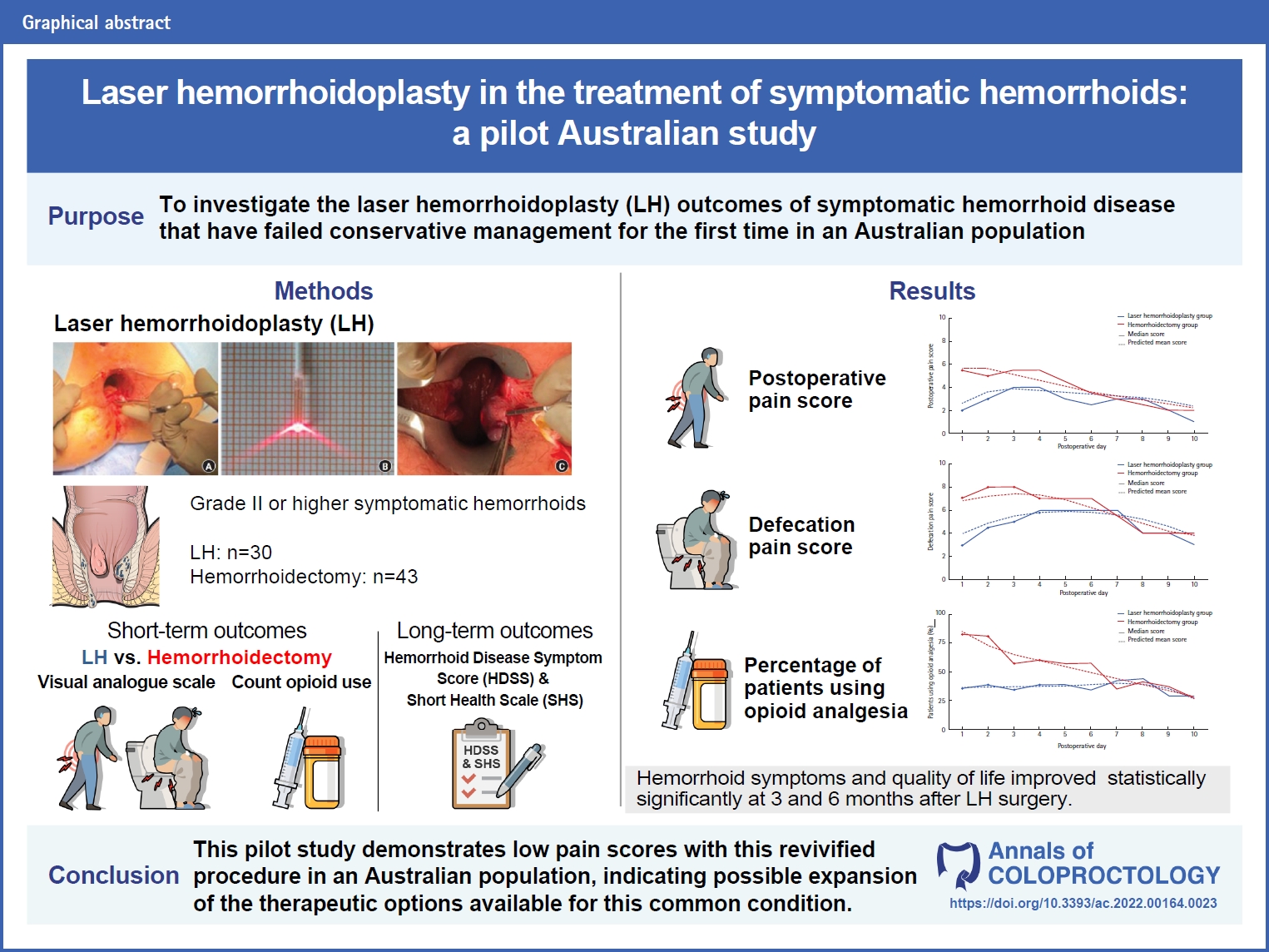
- Laser hemorrhoidoplasty in the treatment of symptomatic hemorrhoids: a pilot Australian study (9,909 times)
- Anshini Jain, Chen Lew, Gamze Aksakal, Richard Hiscock, Naseem Mirbagheri
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(1):52-61. Published online May 19, 2022
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Minimally invasive surgery
- Preoperative localization of potentially invisible colonic lesions on the laparoscopic operation field: using autologous blood tattooing (693 times)
- Ji Yeon Mun, Hyunjoon An, Ri Na Yoo, Hyeon-Min Cho, Bong-Hyeon Kye
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(3):225-233. Published online June 19, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Anorectal benign disease
- Immediate sphincter repair following fistulotomy for anal fistula: does it impact the healing rate and septic complications? (617 times)
- Maher A. Abbas, Anna T. Tsay, Mohammad Abbass
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(3):217-224. Published online June 28, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Colorectal cancer
- Postoperative outcomes after prehabilitation for colorectal cancer patients undergoing surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and nonrandomized studies (1,012 times)
- Ian Jun Yan Wee, Isaac Seow-En, Aik Yong Chok, Eileen Sim, Chee Hoe Koo, Wenjie Lin, Chang Meihuan, Emile Kwong-Wei Tan
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(3):191-199. Published online May 16, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- ERAS
- Clinical impact of a multimodal pain management protocol for loop ileostomy reversal (644 times)
- Jeong Sub Kim, Chul Seung Lee, Jung Hoon Bae, Seung Rim Han, Do Sang Lee, In Kyu Lee, Yoon Suk Lee, In Kyeong Kim
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(3):210-216. Published online June 19, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- A rare presentation of low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm within an amyand’s hernia: a case report (6,419 times)
- Hani Atiqah Saim, Ian Chik, Fahrol Fahmy Jaafar, Zamri Zuhdi, Razman Jarmin, Azlanudin Azman
- Ann Coloproctol. 2023;39(2):183-187. Published online October 18, 2021
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Anorectal benign disease
- Long-term outcomes of sacral neuromodulation for low anterior resection syndrome after rectal cancer surgery (547 times)
- Mario J. de Miguel Valencia, Gabriel Marin, Ana Acevedo, Ana Hernando, Alfonso Álvarez, Fabiola Oteiza, Mario J. de Miguel Velasco
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(3):234-244. Published online June 25, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- ERAS
- Venous thromboembolism among Asian populations with localized colorectal cancer undergoing curative resection: is pharmacological thromboprophylaxis required? A systematic review and meta-analysis (837 times)
- Shih Jia Janice Tan, Emile Kwong-Wei Tan, Yvonne Ying Ru Ng, Rehena Sultana, John Carson Allen, Isaac Seow-En, Ronnie Mathew, Aik Yong Chok
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(3):200-209. Published online May 16, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Technical tips
- Transvaginal removal of rectal stromal tumor with Martius flap interposition: a feasible option for a large tumor at the anterior wall of the rectum (442 times)
- Weerapat Suwanthanma, Ploybutsara Kittiwetsakun, Samart Phuwapraisirisan, Pitichote Hiranyatheb
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(3):276-281. Published online June 26, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Colorectal cancer
- Obstructing colorectal cancer: a population-based review of colonic stenting in Queensland, Australia (435 times)
- Cian Keogh, Julie Moore, Danica Cossio, Nick Smith, David A. Clark
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(3):268-275. Published online June 25, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Partial mesorectal excision can be a primary option for middle rectal cancer: a propensity score–matched retrospective analysis (2,063 times)
- Ee Jin Kim, Chan Wook Kim, Jong Lyul Lee, Yong Sik Yoon, In Ja Park, Seok-Byung Lim, Chang Sik Yu, Jin Cheon Kim
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(3):253-267. Published online March 31, 2023
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Benign proctology,Rare disease & stoma,Surgical technique
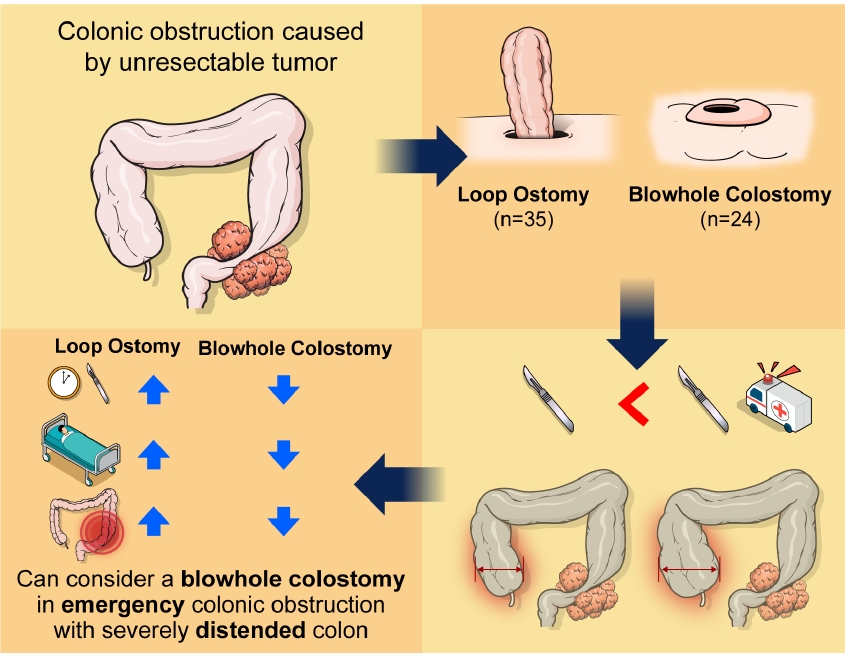
- Comparison of blowhole colostomy and loop ostomy for palliation of acute malignant colonic obstruction (6,671 times)
- Yongjun Park, Dong Uk Choi, Hyung Ook Kim, Yong Bog Kim, Chungki Min, Jung Tack Son, Sung Ryol Lee, Kyung Uk Jung, Hungdai Kim
- Ann Coloproctol. 2022;38(4):319-326. Published online March 7, 2022
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Benign GI diease,Surgical technique
- Double-layered hand-sewn anastomosis: a valuable resource for the colorectal surgeon (7,561 times)
- Cristopher Varela, Manar Nassr, Azharuddin Razak, Nam Kyu Kim
- Ann Coloproctol. 2022;38(3):271-275. Published online March 17, 2022
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF  Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material
- Colorectal cancer
- Colon cancer: the 2023 Korean clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis and treatment (1,859 times)
- Hyo Seon Ryu, Hyun Jung Kim, Woong Bae Ji, Byung Chang Kim, Ji Hun Kim, Sung Kyung Moon, Sung Il Kang, Han Deok Kwak, Eun Sun Kim, Chang Hyun Kim, Tae Hyung Kim, Gyoung Tae Noh, Byung-Soo Park, Hyeung-Min Park, Jeong Mo Bae, Jung Hoon Bae, Ni Eun Seo, Chang Hoon Song, Mi Sun Ahn, Jae Seon Eo, Young Chul Yoon, Joon-Kee Yoon, Kyung Ha Lee, Kyung Hee Lee, Kil-Yong Lee, Myung Su Lee, Sung Hak Lee, Jong Min Lee, Ji Eun Lee, Han Hee Lee, Myong Hoon Ihn, Je-Ho Jang, Sun Kyung Jeon, Kum Ju Chae, Jin-Ho Choi, Dae Hee Pyo, Gi Won Ha, Kyung Su Han, Young Ki Hong, Chang Won Hong, Jung-Myun Kwak, Korean Colon Cancer Multidisciplinary Committee
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(2):89-113. Published online April 30, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF  Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material
- Benign proctology,Postoperative outcome & ERAS,Complication
- Predictors of postoperative urinary retention after semiclosed hemorrhoidectomy (7,867 times)
- Hong Yoon Jeong, Seok Gyu Song, Jong Kyun Lee
- Ann Coloproctol. 2022;38(1):53-59. Published online July 21, 2021
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF