- Search
Article category
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Article category
- Can the Heald anal stent help to reduce anastomotic or rectal stump leak in elective and emergency colorectal surgery? A single-center experience
- Michael Jones, Brendan Moran, Richard John Heald, John Bunni
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(1):82-85. Published online February 26, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Colorectal cancer
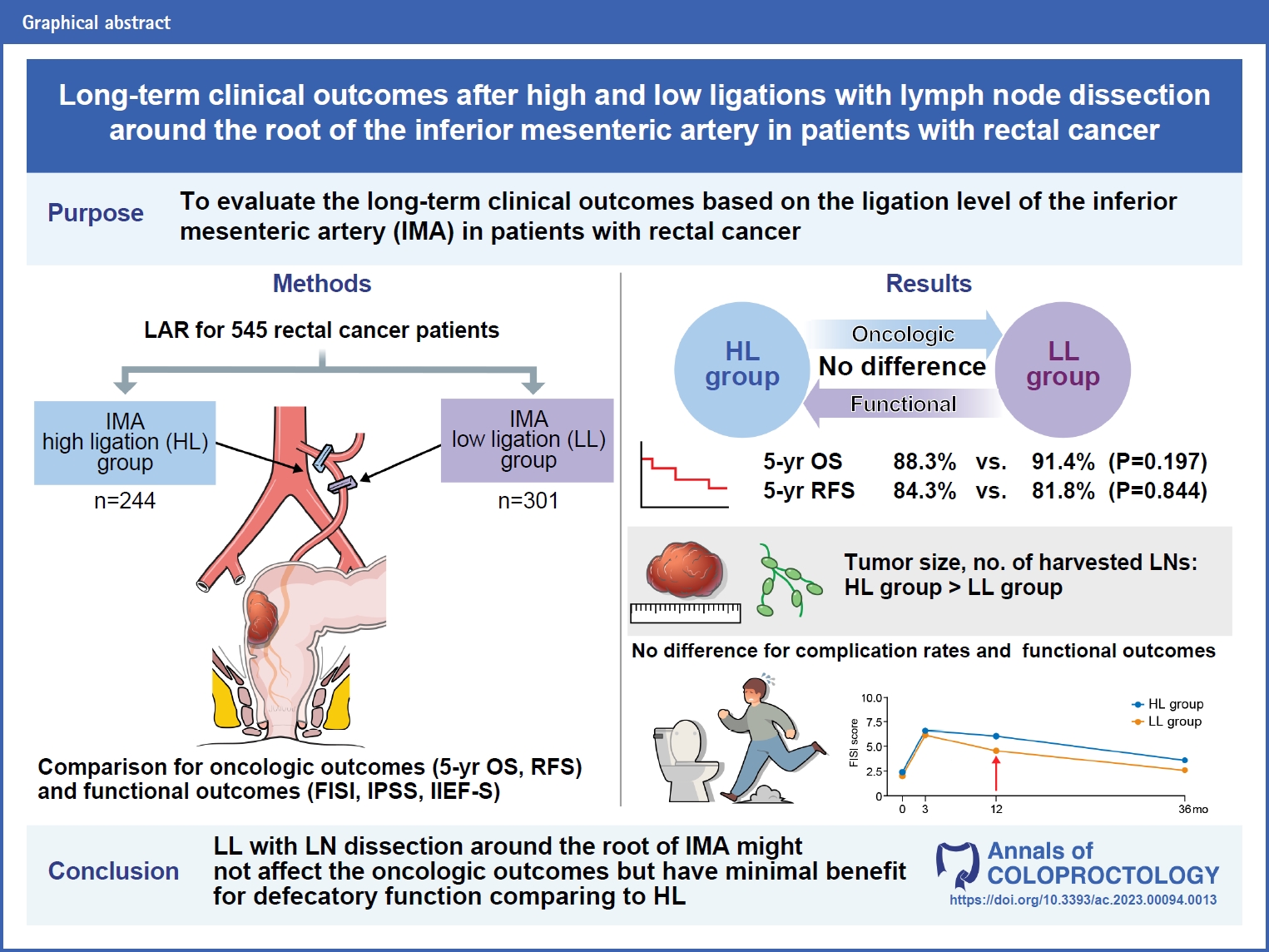
- Long-term clinical outcomes after high and low ligations with lymph node dissection around the root of the inferior mesenteric artery in patients with rectal cancer
- Min Wan Lee, Sung Sil Park, Kiho You, Dong Eun Lee, Dong Woon Lee, Sung Chan Park, Kyung Su Han, Dae Kyung Sohn, Chang Won Hong, Bun Kim, Byung Chang Kim, Hee Jin Chang, Dae Yong Kim, Jae Hwan Oh
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(1):62-73. Published online February 26, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Minimally invasive surgery
- Learning curve for single-port robot-assisted colectomy
- Moon Suk Choi, Seong Hyeon Yun, Sung Chul Lee, Jung Kyong Shin, Yoon Ah Park, Jungwook Huh, Yong Beom Cho, Hee Cheol Kim, Woo Yong Lee
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(1):44-51. Published online December 20, 2022
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Benign bowel disease
- Development of a home health care service platform for ostomy patient management
- Seongwoo Yang, Ji Won Park, Hyuk Hur, Min Jung Kim, Seung-Yong Jeong, Kyounghoon Park, Ik Yong Kim
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(1):36-43. Published online November 21, 2022
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Colorectal cancer
- Long-term bowel functional outcomes following anal sphincter-preserving surgery for upper and middle rectal cancer: a single-center longitudinal study
- Ahmad Sakr, Seung Yoon Yang, Min Soo Cho, Hyuk Hur, Byung Soh Min, Kang Young Lee, Nam Kyu Kim
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(1):27-35. Published online February 28, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Performance reporting design in artificial intelligence studies using image-based TNM staging and prognostic parameters in rectal cancer: a systematic review
- Minsung Kim, Taeyong Park, Bo Young Oh, Min Jeong Kim, Bum-Joo Cho, Il Tae Son
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(1):13-26. Published online February 28, 2024
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Benign bowel disease
- Multimodal prerehabilitation for elderly patients with sarcopenia in colorectal surgery
- Jingting Wu, Hannah Chi, Shawn Kok, Jason M.W. Chua, Xi-Xiao Huang, Shipin Zhang, Shimin Mah, Li-Xin Foo, Hui-Yee Peh, Hui-Bing Lee, Phoebe Tay, Cherie Tong, Jasmine Ladlad, Cheryl H.M. Tan, Nathanelle Khoo, Darius Aw, Cheryl X.Z. Chong, Leonard M.L. Ho, Sharmini S. Sivarajah, Jialin Ng, Winson J.H. Tan, Fung-Joon Foo, Bin-Tean Teh, Frederick H. Koh
- Ann Coloproctol. 2024;40(1):3-12. Published online March 31, 2023
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Tips and tricks for robotic lateral pelvic node dissection
- James Chi-Yong Ngu, Nan-Zun Teo
- Ann Coloproctol. 2023;39(6):531-531. Published online December 26, 2023
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF  Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material
- Minimally invasive surgery
- Robotic natural orifice specimen extraction surgery (NOSES) for anterior resection
- Toan Duc Pham, Tomas Larach, Bushra Othman, Amrish Rajkomar, Alexander G. Heriot, Satish K. Warrier, Philip Smart
- Ann Coloproctol. 2023;39(6):526-530. Published online December 19, 2023
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF  Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material
- Benign bowel disease
- Perioperative considerations for acute appendicitis in patients with COVID-19 infection: two case reports
- In-Kyeong Kim, Seung-jin Kwag, Han-Gil Kim, Young-Tae Ju, Seung-Jun Lee, Tae-Jin Park, Sang-Ho Jeong, Eun-Jung Jung, Jin-Kwon Lee
- Ann Coloproctol. 2023;39(6):521-525. Published online December 7, 2021
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Colorectal cancer
- Computed tomography–assessed presarcopenia and clinical outcomes after laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancer
- Ji Hyeong Song, Rak Kyun Oh, Jeong Eun Lee, Kyung Ha Lee, Ji Yeon Kim, Jin Soo Kim
- Ann Coloproctol. 2023;39(6):513-520. Published online December 12, 2023
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF
- Translational/basic research
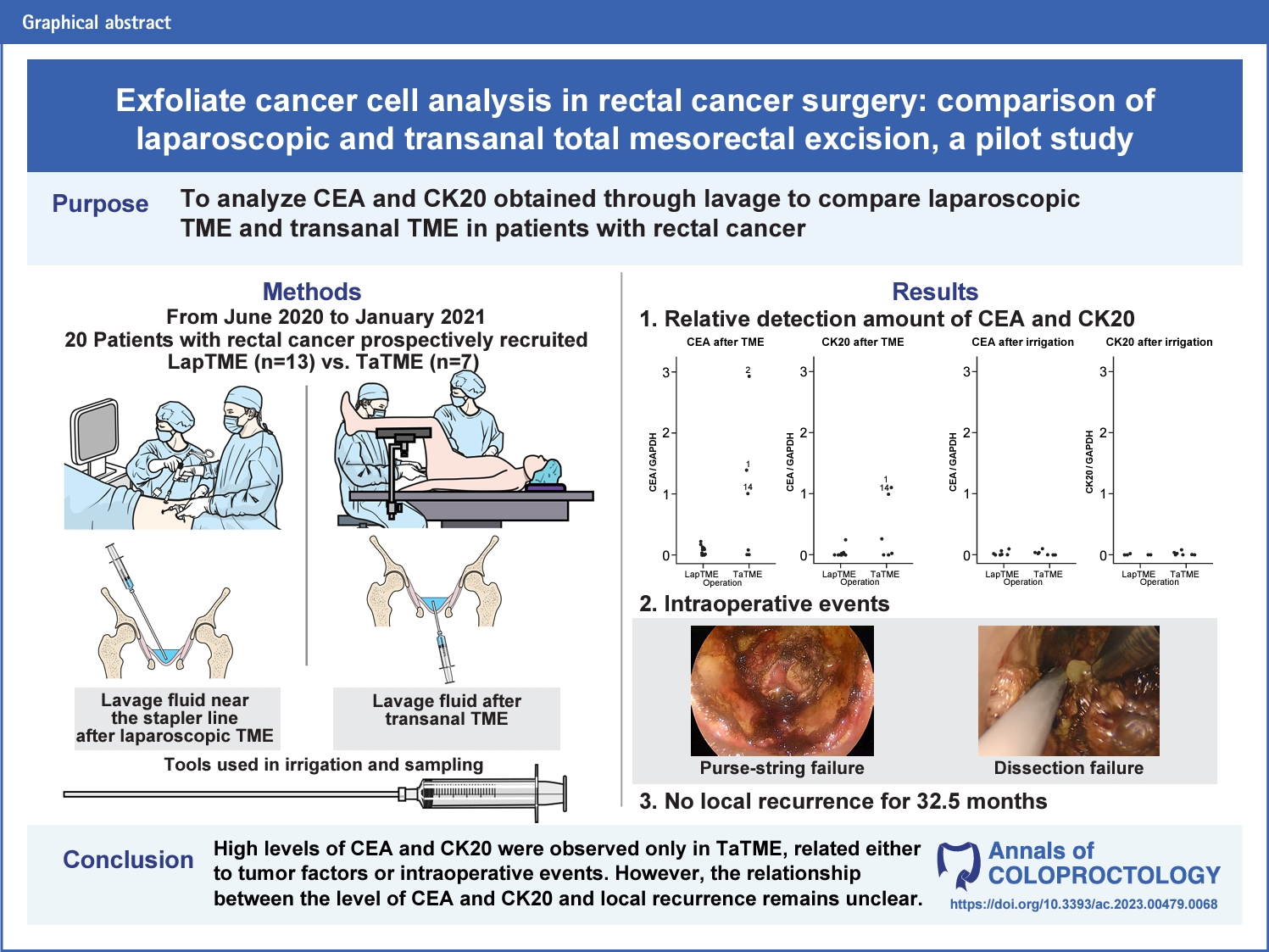
- Exfoliate cancer cell analysis in rectal cancer surgery: comparison of laparoscopic and transanal total mesorectal excision, a pilot study
- Kiho You, Jung-Ah Hwang, Dae Kyung Sohn, Dong Woon Lee, Sung Sil Park, Kyung Su Han, Chang Won Hong, Bun Kim, Byung Chang Kim, Sung Chan Park, Jae Hwan Oh
- Ann Coloproctol. 2023;39(6):502-512. Published online December 26, 2023
-
 Full text
Full text  PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub  Citation
Citation  PDF
PDF  Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material