- Search
| Ann Coloproctol > Volume 40(1); 2024 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Results
Conclusion
Notes
Conflict of interest
Bo Young Oh and Il Tae Son are Editorial Board members of Annals of Coloproctology, but were not involved in in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this article. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Author contributions
Conceptualization: ITS, BJC; Formal analysis: MK, PT; Investigation: MK, PT, MJK, BYO; Methodology: PT; Project administration: ITS, BJC; Supervision: MJK, BYO, Validation: MJK, BYO, Writing–original draft: MK; Writing–review & editing: all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Fig. 1.
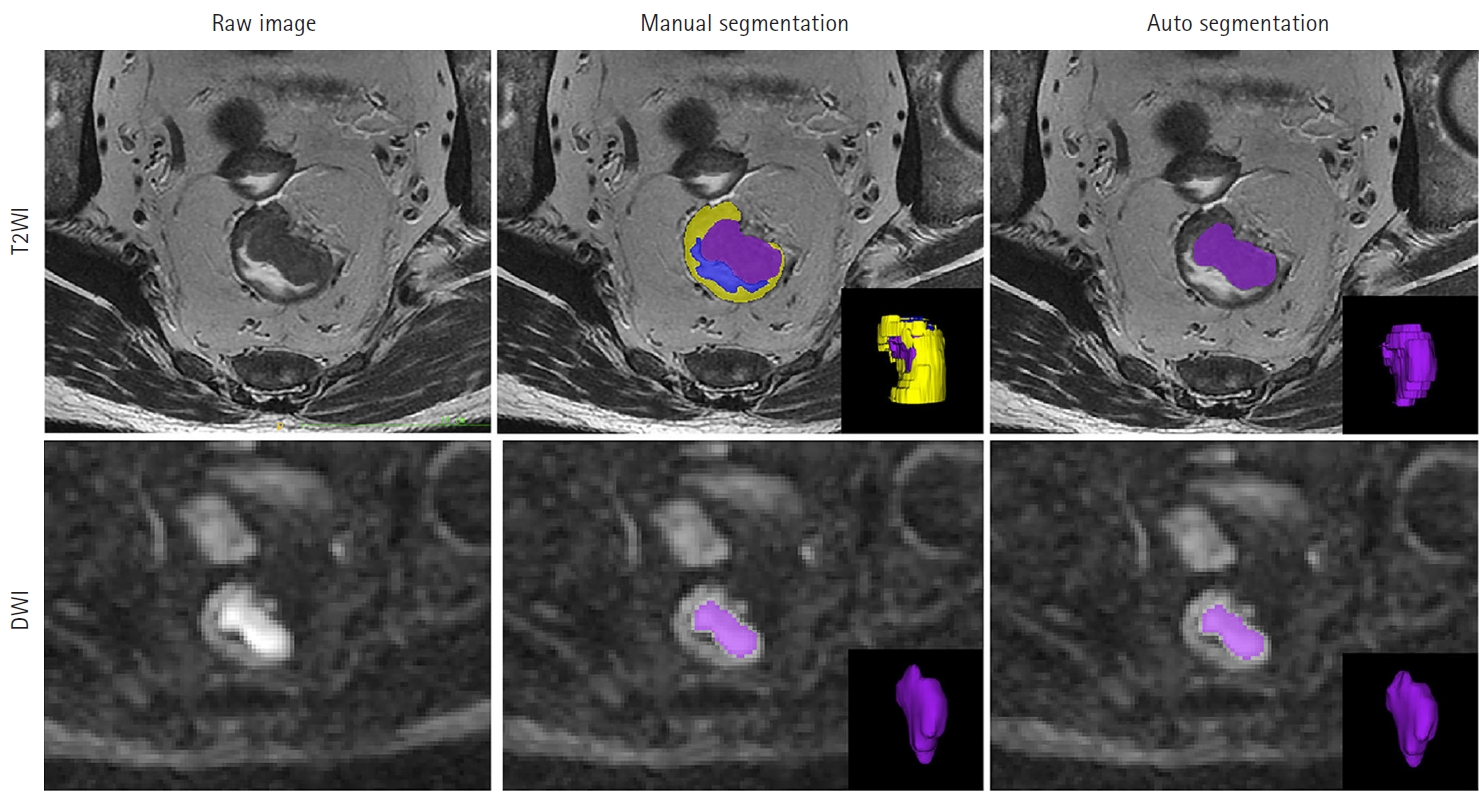
Fig. 2.
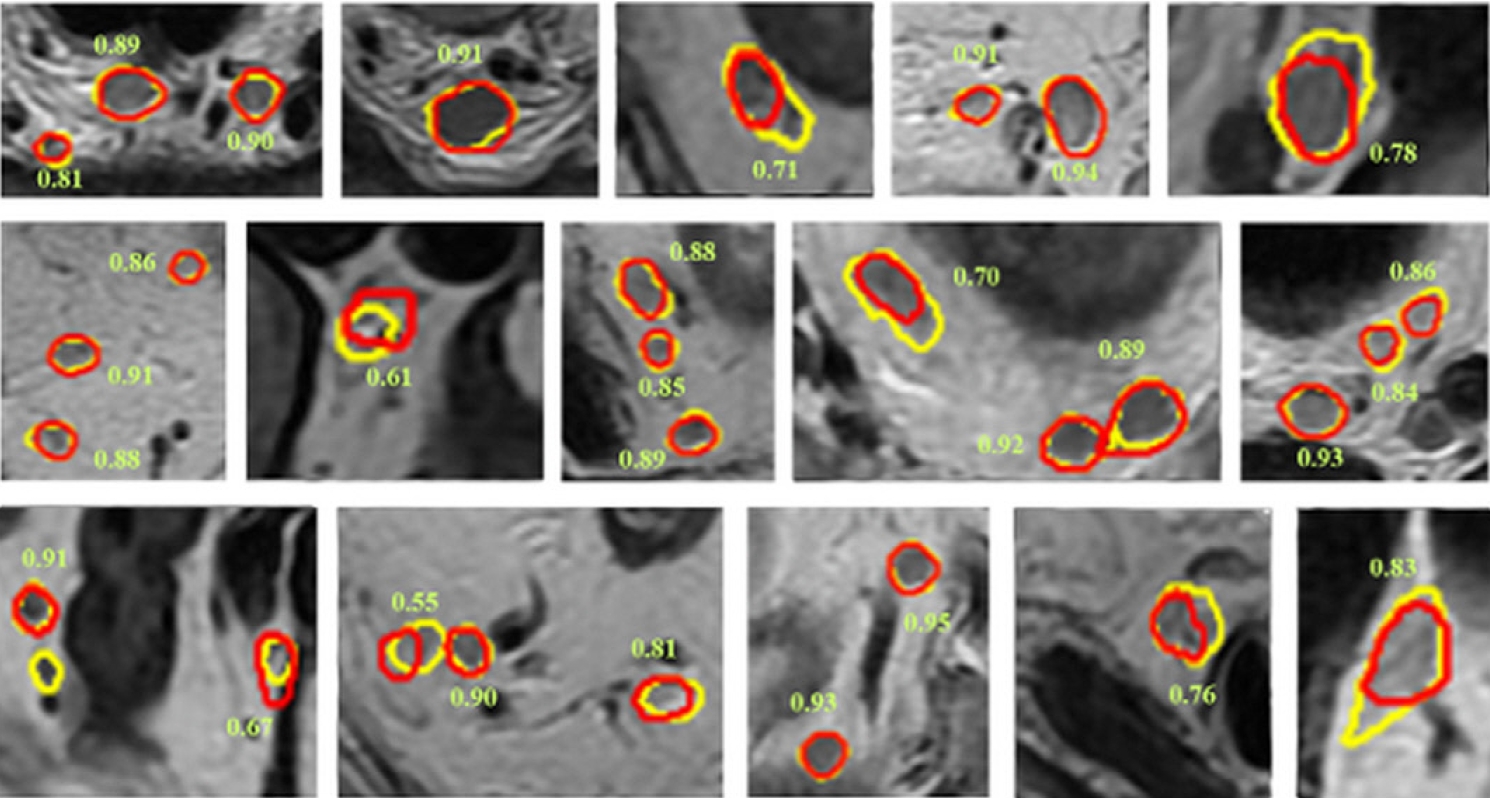
Table 1.
| Study | Country | Modality | Architecture | Internal dataset | External dataset | Automatization | Performance | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor segmentation | ||||||||
| Trebeschi et al. [26] (2017) | The Netherlands | T2WI, DWI | CNN | Training, 56 | None | Manual annotation | DSC, 0.70 | None |
| Validation, 62 | AUROC, 0.99 | |||||||
| Test, 14 | ||||||||
| Wang et al. [27] (2018) | China | T2WI | CNN (2D U-Net) | Training, 84 | None | Manual annotation | DSC, 0.74 | None |
| Validation, 9 | Hausdorff distance, 20.44 | |||||||
| Test, 20 | Average surface distance, 3.25 | |||||||
| Jaccard index, 0.60 | ||||||||
| Kim et al. [28] (2019) | Korea | T2WI | CNN (U-Net, FCN-8, SegNet) | 133 | None | Manual annotation | U-Net: | U-Net is superior to other models |
| DSC, 0.81 | ||||||||
| Sensitivity, 0.79 | ||||||||
| Specificity, 0.98 | ||||||||
| Pang et al. [29] (2021) | China | T2WI | CNN (U-Net) | Training, 88 | 34 | Manual annotation | DSC, 0.95 | None |
| Test, 46 | Sensitivity, 0.97 | |||||||
| Specificity, 0.96 | ||||||||
| Knuth et al. [30] (2022) | Norway | T2WI | CNN (2D U-Net) | 109 | 83 | Manual annotation | DSC, 0.78 | None |
| DeSilvio et al. [31] (2023) | USA | T2WI | CNN (region-specific U-Net, multiclass U-Net) | Training, 44 | 11 | Manual annotation | Region-specific U-Net: | Region-specific U-Net is superior to multiclass U-Net |
| Validation, 44 | DSC, 0.91 | |||||||
| Test, 49 | Hausdorff distance, 2.45 | |||||||
| Zhang et al. [32] (2021) | China | T2WI, DWI | CNN (3D V-Net) | Training, 108 | None | Manual annotation | DSC, 0.96 | None |
| Test, 94 | ||||||||
| Jian et al. [34] (2018) | China | T2WI | CNN (VGG-16) | Training, 410 | None | Fully automatic | DSC, 0.84 | VGG-16 is superior to U-Net |
| Test, 102 | PPV, 0.83 | |||||||
| Sensitivity, 0.88 | ||||||||
| Specificity, 0.97 | ||||||||
| Hammoude distance, 0.27 | ||||||||
| Hausdorff distance, 8.2 | ||||||||
| Zhu et al. [35] (2021) | China | DWI | CNN (3D U-Net) | Training, 180 | None | Fully automatic | DSC, 0.68 | Automatic model is superior to semiautomatic model |
| Validation, 60 | ||||||||
| Test, 60 | ||||||||
| LN segmentation | ||||||||
| Zhao et al. [33] (2020) | China | T2WI, DWI | CNN (Mask R-CNN) | 293 | 50 | Manual annotation | Detection: | Mask R-CNN is superior to junior radiologists in LN detection |
| Sensitivity, 0.63 | ||||||||
| PPV, 0.65 | ||||||||
| False-positive rate per case, 8.2 | ||||||||
| Segmentation: | ||||||||
| DSC, 0.81-0.82 |
T2WI, T2-weighted image; DWI, diffusion-weighted image; CNN, convolutional neural network; DSC, dice similarity coefficient; AUROC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; 2D, 2-dimensional; FCN-8, fully convolutional network (8 pixels); 3D, 3-dimensional; LN, lymph node; PPV, positive predictive value.
Table 2.
| Study | Country | Modality | Architecture | Internal dataset | External dataset | Performance | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T stage | |||||||
| Kim et al. [28] (2019) | Korea | T2WI | CNN (AlexNet, Inception) | 133 | None | Inception: | Inception is superior to AlexNet |
| Accuracy, 0.94 | |||||||
| Sensitivity, 0.88 | |||||||
| Specificity, 1.0 | |||||||
| Wu et al. [43] (2021) | China | T2WI | CNN (Faster R-CNN) | 183 | None | Coronal view: | None |
| AUROC (T1), 0.96 | |||||||
| AUROC (T2), 0.97 | |||||||
| AUROC (T3), 0.97 | |||||||
| AUROC (T4), 0.97 | |||||||
| N stage | |||||||
| Lu et al. [44] (2018) | China | T2WI, DWI | CNN (Faster R-CNN) | 351 | 414 | AUROC, 0.91 | No difference in accuracy compared to radiologists |
| Diagnostic time, 20 sec vs. 600 sec | Faster than radiologists | ||||||
| Ding et al. [45] (2019) | China | T2WI, DWI | CNN (Faster R-CNN) | 414 | None | κ coefficient: | AI model is superior to radiologists |
| AI vs. pathologist, 0.57 | |||||||
| Radiologist vs. pathologist, 0.47 | |||||||
| Zhou et al. [46] (2019) | China | Pelvic HD MRI | CNN | Training, 201 | None | AUROC, 0.89 | No difference in accuracy compared with radiologists |
| Test, 100 | Diagnostic time, 10 sec vs. 600 sec | Faster than radiologists | |||||
| Li et al. [47] (2021) | China | T2WI | CNN (InceptionV3) | 129 | None | Sensitivity, 0.95 | AI is superior to radiologists |
| Specificity, 0.95 | |||||||
| PPV, 0.95 | |||||||
| NPV, 0.95 | |||||||
| AUROC, 0.99 | |||||||
| Circumferential resection margin | |||||||
| Wang et al. [48] (2020) | China | T2WI | CNN (Faster R-CNN) | Training, 192 | None | Accuracy, 0.93 | None |
| Test, 48 | Sensitivity, 0.84 | ||||||
| Specificity, 0.96 | |||||||
| AUROC, 0.95 | |||||||
| Xu et al. [49] (2020) | China | T2WI | CNN (Faster R-CNN) | Training, 300 | None | Accuracy, 0.88 | None |
| Test, 50 | Sensitivity, 0.86 | ||||||
| Specificity, 0.90 | |||||||
| AUROC, 0.93 | |||||||
Table 3.
| Study | Country | Modality | Architecture | Internal dataset | External dataset | Performance | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsatellite instability | |||||||
| Zhang et al. [61] (2021) | China | T2WI | CNN (3D MobileNetV2) | Training, 395 | None | Image model: | Image model is superior to clinical model |
| Validation, 395 | Sensitivity, 0.89 | ||||||
| Test, 96 | Specificity, 0.74 | ||||||
| AUROC, 0.82 | |||||||
| Clinical model: | |||||||
| Sensitivity, 1.00 | |||||||
| Specificity, 0.31 | |||||||
| AUROC, 0.61 | |||||||
| Cao et al. [62] (2023) | China | Enhanced APCT | CNN (Resnet101) | Training, 1,124 | 206 | Internal validation: | None |
| Test, 482 | Accuracy, 0.99 | ||||||
| Sensitivity, 1.0 | |||||||
| Specificity, 0.97 | |||||||
| AUROC, 0.99 | |||||||
| External validation: | |||||||
| Accuracy, 0.91 | |||||||
| Sensitivity, 0.90 | |||||||
| Specificity, 0.93 | |||||||
| AUROC, 0.92 | |||||||
| KRAS mutation | |||||||
| He et al. [63] (2020) | China | Enhanced APCT | CNN (ResNet) | Training, 117 | None | AI model: | AI model is superior to radiomics model |
| Test, 40 | Sensitivity, 0.59 | ||||||
| Specificity, 1.0 | |||||||
| AUROC, 0.93 | |||||||
| Radiomics model: | |||||||
| Sensitivity, 0.70 | |||||||
| Specificity, 0.85 | |||||||
| AUROC, 0.82 | |||||||
Table 4.
| Study | Country | Modality | Architecture | Internal dataset | External dataset | Performance | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shi et al. [79] (2019) | China | T2WI (pre- and mid-CRT) | CNN | 51 | None | pCR: | No difference in predicting pCR |
| AUROC (CNN), 0.83 | CNN model is inferior to radiomics model in predicting GR | ||||||
| AUROC (radiomics), 0.81 | |||||||
| GR: | |||||||
| AUROC (CNN), 0.74 | |||||||
| AUROC (radiomics), 0.92 | |||||||
| Zhang et al. [80] (2020) | China | T2WI (pre- and post-CRT) | CNN (models A, B, C) | Training, 290 | 93 | pCR: | Model A is superior to the other models |
| Accuracy, 0.98 | |||||||
| Sensitivity, 1.00 | |||||||
| Specificity, 0.97 | |||||||
| AUROC, 0.99 | |||||||
| Zhu et al. [81] (2020) | China | T2WI (pre-CRT) | CNN | Training, 400 | None | GR: | None |
| Validation, 100 | Sensitivity, 0.93 | ||||||
| Test, 200 | Specificity, 0.62 | ||||||
| AUROC, 0.81 | |||||||
| Jang et al. [78] (2021) | Korea | T2WI (post-CRT) | CNN (ShuffleNet) | Training, 303 | None | pCR: | AI model is superior to human for predicting pCR and GR |
| Validation, 46 | Accuracy, 0.85 | ||||||
| Test, 117 | Sensitivity, 0.30 | ||||||
| Specificity, 0.96 | |||||||
| GR: | |||||||
| Accuracy 0.72 | |||||||
| Sensitivity 0.54 | |||||||
| Specificity 0.81 |