- Search
| Ann Coloproctol > Volume 39(4); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Hemorrhoids are the most common benign anorectal diseases. Mucopexy strengthens the anal canal mucosa, which can be performed alone or in combination with Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation (DG-HAL). In this study, we compared the postoperative complications between simple mucopexy plus HAL with and without a Doppler guide.
Methods
This study was performed as a single-blinded randomized clinical trial. Patients referred to a tertiary colorectal referral clinic with grades 3 and 4 hemorrhoids who were candidates for surgical intervention entered the study. Thirty-six patients were randomly divided into 2 groups. Group A including 18 patients underwent mucopexy and DG-HAL and the other 18 patients (group B) underwent standard mucopexy and HAL without a Doppler guide. Postoperative pain score and the duration of oral analgesic consumption were recorded. Additionally, postoperative symptoms and complications were recorded and compared between the 2 methods.
Results
There was no significant difference between the 2 groups in terms of pain score and the duration of postoperative analgesic consumption as well as the incidence of postoperative complications. Besides, the primary grade of hemorrhoids was not significantly associated with recurrence, but there was a significant association between body mass index and Wexner score (WS) with recurrence. The mean WS of patients showed a significant decrease in both groups postoperatively. However, the rate of WS reduction was not remarkably different between the 2 groups.
Hemorrhoids are the most common benign anorectal diseases caused by disruption of the supporting structures and vascular cushions of the anal canal which is affecting millions of people worldwide [1, 2]. Numerous factors such as gastrointestinal problems, chronic constipation, lifestyle, diet, and daily activity are associated with its incidence [3, 4]. Internal hemorrhoids are divided into 4 grades based on the “Goligher classification” which is depended on the severity of prolapse and its reducibility [3, 5, 6].
Hemorrhoidectomy as an invasive surgical method is considered the gold standard approach for the treatment of severe symptomatic hemorrhoids; however, minimally invasive surgical procedures have been introduced in the last 2 decades to reduce postoperative complications and improve patient satisfaction [7–11]. Mucopexy and Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation (DG-HAL) techniques have been recently emerged for the effective management of prolapsing hemorrhoids [12–16].
DG-HAL was first proposed by Morinaga et al. [17] with a proctoscope in conjunction with a Doppler transducer as a non-excisional surgical option. DG-HAL tries to ligate distal branches of the superior rectal artery and patent venous drainage reducing blood flow of the hemorrhoidal plexus [13, 17, 18].
Recent study demonstrates the possibility of HAL without use of Doppler [19] and this study showed the possibility of this approach and adding Doppler did not change the outcome significantly.
In this prospective randomized controlled trial, we aimed to compare postoperative complications, recurrence rates, the duration of analgesic consumption, and pain score after surgery between simple mucopexy plus HAL with and without a Doppler guide. Additionally, we investigated the factors affecting the recurrence of hemorrhoids during the follow-up visits.
This was a prospective, single-blinded randomized controlled trial. The study protocol was in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration at all stages, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Iran University of Medical Sciences, Firoozgar Clinical Research Development Center (No. IR.IUMS.FMD.REC.1398.167) and registered at Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (No. IRCT201909- 27044897N1). Informed written consent was obtained from all patients before the operation.
Patients with symptomatic grades 3 and 4 internal hemorrhoids referred to colorectal clinic of Firoozgar Hospital (a tertiary colorectal referral center in Tehran, Iran) were enrolled in this study from July 2019 to October 2020. Experienced colorectal surgeon confirmed the diagnosis of grades 3 and 4 hemorrhoids through physical examination (digital rectal examination) and anoscopy. Participants with a previous history of surgical interventions for hemorrhoids or other proctologic conditions like inflammatory bowel disease, Solitary rectal ulcer and fistula in ano, presence of non-hemorrhoidal anorectal mass, thrombosed hemorrhoids and anal fissures were excluded.
The chief complaint of all patients such as rectal bleeding, protrusion of the anus, pain during defecation, etc., were obtained through history taking at the first visit. Moreover, patients’ characteristics including age, sex, weight, height, and body mass index (BMI) were recorded. The initial Wexner score (WS) of patients (from 0 to 20) was recorded as well.
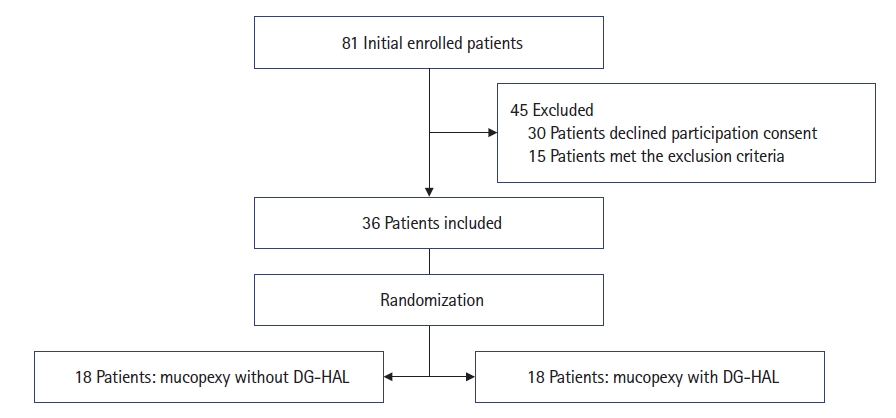
As shown in Fig. 1, initially 81 patients were enrolled in the study; 30 patients declined entering the study and 15 patients were excluded because of concomitant pathology such as fistula, thrombosed hemorrhoids, and chronic fissures. The 36 remained patients were randomly divided into 2 groups. Group A including 18 patients underwent DG-HAL-rectoanal repair (DG-HAL-RAR). In fact, vessels located around the circumference in the right posterolateral, right mid-lateral, right anterolateral, left anterolateral, left mid-lateral, and left posterolateral (1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11 o’clock) positions were ligated under a Doppler guide. Also, mucopexy was performed at 1, 5, 7, and 11 o’clock. However, patients in group B including 18 patients underwent mucopexy and rectoanal repair at standard areas mentioned above without using a Doppler guide. Arterial ligation was also performed at standard zones. In order to have the same procedure for both groups, the DG-HAL-RAR device was used as a retractor but Doppler was not activated.
All surgical procedures were performed by the same surgeon and operating team. Only participants were blinded to the surgical method. Simple randomization was performed using sealed envelopes.
The device used for DG-HAL procedure was an anoscope equipped with a Doppler probe at the tip (Trilogy TRI2010, A.M.I GmbH). Up to 6 vessels ligation was done during this method. Patients were instructed for postoperative recovery and discharged on the operation day with adequate nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Initial assessment was performed to define postoperative pain score at 48 hours postoperatively using visual analogue scale in which zero indicates absence of pain, while 10 represents the most intense pain possible [20]. In addition, the duration of analgesic consumption was asked at 14 days after surgery by a telephone call. Further follow-ups were performed at 1, 3, and 6 months after surgery through history taking and physical examination. Incidence of postoperative complications including bleeding, infection evidences like perianal abscess formation and purulent discharge, gas incontinence, fecal incontinence, anal stricture, and recurrence of prolapsing hemorrhoids were assessed during these intervals.
All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 26 (IBM Corp). Demographic data presented as mean±standard deviation or crude numbers with frequency. Normal distribution of data was tested using Shapiro-Wilk test. Pearson chi-square or Fisher exact test was used to assess nominal variables between the groups. Mann-Whitney U-test was also used when appropriate. A P-value below 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Baseline demographic characteristics of the study subjects are presented in Table 1. The main complaints by patients before the operation were bleeding (63.9%), protrusion (19.4%), pain during defecation (13.9%), and constipation (2.8%). At 48 hours after the operation, in group B, the mean pain score of patients was 7.06±1.58 versus 6.67±1.49 in patients in group A with no significant difference (P=0.406). At 14 days, the duration of oral analgesics consumption days did not differ significantly between the 2 groups (8.33±2.24 in group B vs. 8.72±2.49 in group A, P=0.696). Further follow-ups at 1, 3, and 6 months after the operation were performed in all 36 patients. No patients were lost to follow up. The study flowchart is depicted in Fig. 1.
Infection was not found in any patient at 3 and 6 months. At 1 month, bleeding occurred in 7 patients, 4 (22.2%) in group B and 3 (16.7%) in group A (P>0.999). No patients represented with bleeding at 3-month visit but bleeding was found in one patient at 6-month which was in group B.
Moreover, gas incontinency was reported in 4 patients (22.2%) in group B and 2 (11.1%) in group A at 1 month but did not differ statistically between the 2 methods (P=0.658). Fecal incontinency (soilage) was found in 3 patients only at 1 month (11.1% in group B and 5.6% in group A, P>0.999). No significant differences were found between the 2 methods regarding the occurrence of anal stricture (Table 2). No recurrence of hemorrhoids was reported at 1 month in any patient by physical examination. At 3-month visit, recurrent hemorrhoids were detected in 2 patients in group B (P=0.486) and in 1 patient (5.6%) in group A, which was not statistically significant. The initial grade of hemorrhoid, BMI and initial WS were analyzed regarding the risk of recurrence. Hemorrhoid grade (3 or 4) had no significant effect on the recurrence regardless of the surgical method (P=0.069 in group A and P=0.183 in group B), but there was a significant association between initial WS and recurrence (P=0.010 in group A and P=0.013 in group B). Furthermore, BMI had a significant association with hemorrhoid recurrence (P=0.005 in group A and P=0.013 in group B). Table 3 demonstrates the summery of recurrence risk factors.
The mean WS was measured at 5.27±2.88 in group A and 4.61±3.03 in group B before surgery. Postoperative WS (2.11±1.56 in group A vs. 2.66±2.49 in group B) decreased significantly in both groups (P<0.001 in both groups), though the extent of decrease did not differ significantly between the 2 groups (P=0.397).
In this investigation, we compared the postoperative outcomes and complications of mucopexy plus blind HAL (without Doppler guide) with DG-HAL-RAR. Both groups underwent the procedure using the same device; however, Doppler guide was not activated in group B patients. In fact, the device was used only as a retractor in group B. We also evaluated the factors affecting hemorrhoid recurrence including initial grade of hemorrhoid, initial WS and BMI. Based on our results, there was no significant difference between the 2 surgical treatments regarding postoperative complications at 1, 3, and 6 months. However, the pain score and the duration of oral analgesic consumption at 14 days were lower in mucopexy and DG-HAL, but this difference was not significant.
BMI was reported as one of the risk factors for recurrence in our study; however, previous studies did not show obesity as a risk factor of recurrent external hemorrhoid [21]. Our study also showed the higher incidence of recurrence in the patient with higher WS one of the explanations for this could be the presence of occult mucosal rectal prolapse [22]. Indeed, we found obesity may be as a potential risk factor of hemorrhoid recurrence, while other studies did not reveal such finding. Hence, we propose further studies on a larger population for evaluation of obesity as a risk factor for recurrence of hemorrhoid. Several studies have been performed to determine the advantages and disadvantages of surgical methods in the management of hemorrhoids [23–26].
Mucopexy alone [27] or in combination with DG-HAL is one of the evolving methods widely used by surgeons to treat hemorrhoids instead of removing the hemorrhoidal tissue by previous invasive procedures like hemorrhoidectomy. Less postoperative pain, bleeding, and tissue damage during the operation, shorter time of the operation, and fewer postoperative complications are some of the reasons advocating the new methods [12, 25, 28, 29].
In the early 1970s, the role of arterial flow and arteriovenous anastomoses in the pathogenesis of hemorrhoids was recognized. In 1994, Galkin et al. [30] effectively treated hemorrhoids by endovascular catheterization of the superior hemorrhoidal artery and embolization of its distal branches. Thereafter, in 1995, Morinaga et al. [17] reported an alternative method for treating hemorrhoids by hemorrhoidal dearterialization using a specially designed proctoscope coupled with a Doppler transducer to identify the hemorrhoidal arteries. Thereafter, mucopexy was added to DG-HAL and DG-HAL-RAR using transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization device was introduced.
As described previously, other modifications in DG-HAL-RAR method is published in the literature. Mucopexy alone has been shown to be effective in treating patient symptoms [27] blind HAL also used [19] and seems to be effective in treating hemorrhoid symptoms.
Omitting Doppler localization of arteries and blind ligation is becoming popular in the literature. The significance of present study is the location of blind HAL, which is different from a previous report [19]. This previous study ligated the vessels in 3 points, but regarding previous observations detecting the pulse in 6 points, we intended to perform ligation at 6 points.
This study has some limitations, the sample size is low and this might be one of the descriptions of nonsignificant differences that were observed. Unfortunately, the operative time was not compared which might be different in 2 groups. Since the procedures were done by one surgeon, blinding the surgeon was practically not possible but the physician that was evaluating the patient’s postoperative course was blind. So the authors highly recommend a large size double-blind study to compare blind HAL using 3 points or 6 points ligation with longer follow-up.
In conclusion, mucopexy with DG-HAL is a more expensive treatment than simple mucopexy. According to the similar therapeutic outcomes, recurrence rate, and postoperative complications between the 2 groups, simple mucopexy and rectoanal repair with blind HAL (without Doppler guide) at standard zones (1, 5, 7, and 11 o’clock) could be considered for the treatment of grades 3 and 4 hemorrhoids effectively.
Notes
Author contributions
Conceptualization: MA, AA; Data curation: M Moradi, SS; Formal analysis: MR; Investigation: M Masoodi, SA; Methodology: M Moradi, MR; Project administration: MR; Resources: MA; Software: AA; Supervision: MA, AA; Validation: SA, M Masoodi; Visualization: MA, SS; Writing–original draft: MA, SS; Writing–review & editing: all authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Table 1.
Baseline demographic characteristics of the study subjects (n=36)
Table 2.
Postoperative variables and complications between the mucopexy with and without DG-HAL (n=36)
REFERENCES
1. Riss S, Weiser FA, Schwameis K, Riss T, Mittlböck M, Steiner G, et al. The prevalence of hemorrhoids in adults. Int J Colorectal Dis 2012;27:215–20.


2. Thomson JP, Leicester RJ, Smith LE. Haemorrhoids. In: Henry MM, Swash M, editors. Coloproctology and the pelvic floor. 2nd ed. Butterworth-Heinemann; 1992. p. 373–93.
3. Loder PB, Kamm MA, Nicholls RJ, Phillips RK. Haemorrhoids: pathology, pathophysiology and aetiology. Br J Surg 1994;81:946–54.


4. Talley NJ, Lasch KL, Baum CL. A gap in our understanding: chronic constipation and its comorbid conditions. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;7:9–19.


5. Cataldo P, Ellis CN, Gregorcyk S, Hyman N, Buie WD, Church J, et al. Practice parameters for the management of hemorrhoids (revised). Dis Colon Rectum 2005;48:189–94.


6. Lohsiriwat V. Hemorrhoids: from basic pathophysiology to clinical management. World J Gastroenterol 2012;18:2009–17.


7. Ganz RA. The evaluation and treatment of hemorrhoids: a guide for the gastroenterologist. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;11:593–603.


8. Guttenplan M. The evaluation and office management of hemorrhoids for the gastroenterologist. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2017;19:30.


9. Picchio M, Greco E, Di Filippo A, Marino G, Stipa F, Spaziani E. Clinical outcome following hemorrhoid surgery: a narrative review. Indian J Surg 2015;77(Suppl 3): 1301–7.



10. Rivadeneira DE, Steele SR, Ternent C, Chalasani S, Buie WD, Rafferty JL, et al. Practice parameters for the management of hemorrhoids (revised 2010). Dis Colon Rectum 2011;54:1059–64.


11. Sneider EB, Maykel JA. Diagnosis and management of symptomatic hemorrhoids. Surg Clin North Am 2010;90:17–32.


12. Abudeeb H, Ugwu A, Darabnia J, Hammad A, Khan K, Maung M, et al. THD and mucopexy: efficacy and controversy. Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2017;21:89–92.



13. Dal Monte PP, Tagariello C, Sarago M, Giordano P, Shafi A, Cudazzo E, et al. Transanal haemorrhoidal dearterialisation: nonexcisional surgery for the treatment of haemorrhoidal disease. Tech Coloproctol 2007;11:333–9.


14. Faucheron JL, Poncet G, Voirin D, Badic B, Gangner Y. Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation and rectoanal repair (HAL-RAR) for the treatment of grade IV hemorrhoids: long-term results in 100 consecutive patients. Dis Colon Rectum 2011;54:226–31.


15. Forrest NP, Mullerat J, Evans C, Middleton SB. Doppler-guided haemorrhoidal artery ligation with recto anal repair: a new technique for the treatment of symptomatic haemorrhoids. Int J Colorectal Dis 2010;25:1251–6.


16. Gallo G, Martellucci J, Sturiale A, Clerico G, Milito G, Marino F, et al. Consensus statement of the Italian Society of Colorectal Surgery (SICCR): management and treatment of hemorrhoidal disease. Tech Coloproctol 2020;24:145–64.



17. Morinaga K, Hasuda K, Ikeda T. A novel therapy for internal hemorrhoids: ligation of the hemorrhoidal artery with a newly devised instrument (Moricorn) in conjunction with a Doppler flowmeter. Am J Gastroenterol 1995;90:610–3.

18. Zagriadskiĭ EA. Transanal Doppler-guided desarterization with mucopexy (HAL-RAR) for the treatment of hemorrhoids stage III-IV. Khirurgiia (Mosk) 2013;(4):59–64.
19. Perivoliotis K, Spyridakis M, Zintzaras E, Arnaoutoglou E, Pramateftakis MG, Tepetes K. Non-Doppler hemorrhoidal artery ligation and hemorrhoidopexy combined with pudendal nerve block for the treatment of hemorrhoidal disease: a non-inferiority randomized controlled trial. Int J Colorectal Dis 2021;36:353–63.


20. Gould D, Kelly D, Goldstone L, Gammon J. Examining the validity of pressure ulcer risk assessment scales: developing and using illustrated patient simulations to collect the data. J Clin Nurs 2001;10:697–706.


21. Greenspon J, Williams SB, Young HA, Orkin BA. Thrombosed external hemorrhoids: outcome after conservative or surgical management. Dis Colon Rectum 2004;47:1493–8.


22. Bouchard D, Abramowitz L, Castinel A, Suduca JM, Staumont G, Soudan D, et al. One-year outcome of haemorrhoidectomy: a prospective multicentre French study. Colorectal Dis 2013;15:719–26.


23. Béliard A, Labbé F, de Faucal D, Fabreguette JM, Pouderoux P, Borie F. A prospective and comparative study between stapled hemorrhoidopexy and hemorrhoidal artery ligation with mucopexy. J Visc Surg 2014;151:257–62.


24. Lucarelli P, Picchio M, Caporossi M, De Angelis F, Di Filippo A, Stipa F, et al. Transanal haemorrhoidal dearterialisation with mucopexy versus stapler haemorrhoidopexy: a randomised trial with long-term follow-up. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2013;95:246–51.



25. Tsang YP, Fok KL, Cheung YS, Li KW, Tang CN. Comparison of transanal haemorrhoidal dearterialisation and stapled haemorrhoidopexy in management of haemorrhoidal disease: a retrospective study and literature review. Tech Coloproctol 2014;18:1017–22.


26. Zhai M, Zhang YA, Wang ZY, Sun JH, Wen J, Zhang Q, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing suture-fixation mucopexy and Doppler-guided hemorrhoidal artery ligation in patients with grade III hemorrhoids. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2016;2016:8143703.



27. Aigner F, Kronberger I, Oberwalder M, Loizides A, Ulmer H, Gruber L, et al. Doppler-guided haemorrhoidal artery ligation with suture mucopexy compared with suture mucopexy alone for the treatment of grade III haemorrhoids: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Colorectal Dis 2016;18:710–6.


28. Trenti L, Biondo S, Kreisler Moreno E, Sanchez-Garcia JL, Espin-Basany E, Landaluce-Olavarria A, et al. Short-term outcomes of transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization with mucopexy versus vessel-sealing device hemorrhoidectomy for grade III to IV hemorrhoids: a prospective randomized multicenter trial. Dis Colon Rectum 2019;62:988–96.


29. Walega P, Krokowicz P, Romaniszyn M, Kenig J, Sałówka J, Nowakowski M, et al. Doppler guided haemorrhoidal arterial ligation with recto-anal-repair (RAR) for the treatment of advanced haemorrhoidal disease. Colorectal Dis 2010;12(10 Online): e326–9.


30. Galkin EV. Interventional radiology of chronic hemorrhoids. Vestn Rentgenol Radiol 1994;(4):52–6.
- TOOLS