Perioperative Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen Ratio Is a Prognostic Indicator in Patients With Stage II Colorectal Cancer
Article information
Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate whether the perioperative carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) ratio could be used as a determinant for adjuvant therapy after curative surgery in stage II colorectal cancer.
Methods
Data for 119 patients with stage II colorectal cancer who underwent radical surgery between 2010 and 2013 were collected. The perioperative CEA ratio was defined as the postoperative/preoperative serum CEA level, and the patients were grouped according to their perioperative CEA ratios: high ratio (≥0.5) and low ratio (<0.5). Overall survival rates were calculated, and their prognostic significances were analyzed.
Results
The overall survival rates of the high and the low perioperative CEA groups were 68.2% and 86.8%, respectively (P = 0.033). In patients with normal preoperative CEA levels (<5 ng/mL), the high perioperative CEA ratio group showed a worse survival rate than the low perioperative CEA ratio group (71.7% vs. 100.0%, P = 0.007). In patients with high preoperative CEA levels (≥5 ng/mL), the high perioperative CEA ratio group showed a worse survival rate than the low perioperative CEA ratio group (33.3% vs. 75.0%, P = 0.036). In the multivariate analysis, perioperative CEA ratio (P = 0.046), age (P = 0.034), and venous invasion (P = 0.015) were independent prognostic factors for survival.
Conclusion
The perioperative CEA ratio is a prognostic indicator for stage II colorectal cancer. Patients with normal preoperative serum CEA levels might also be considered for adjuvant therapy if their perioperative CEA ratios are higher than 0.5.
INTRODUCTION
Colorectal cancer is the fourth leading cause of death from cancer in Korea, with a crude mortality rate of 16.4/100,000 [1]. Although the age-standardized incidence rate of colorectal cancer decreased from 2011 to 2014, it is still the third most frequently diagnosed cancer. The standardized treatment for nonmetastatic colorectal cancer is the radical resection of the tumor lesion. In patients with stage III (node-positive) disease, adjuvant chemotherapy is a routine therapy, and the benefits of chemotherapy have been clearly demonstrated [2]. The administration of chemotherapy in patients with stage II colorectal cancer (node-negative) remains controversial, but those with risk factors for recurrence are recommended for adjuvant chemotherapy [3].
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is one of the most readily accessible tumor markers for colorectal cancer. Increased preoperative serum CEA levels are related with an increased risk of recurrence and poor prognosis [456]. However, in 2006, the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) concluded that the evidence for using preoperative CEA levels as guidance for adjuvant chemotherapy was insufficient [7]. As studies on CEA have progressed, Lin et al. [8] reported that high early postoperative CEA levels are associated with early relapse of CRC and that early postoperative CEA values should surpass preoperative CEA values as a prognostic indicator. Others have confirmed the perioperative serum CEA change as a useful prognostic factor in patients with colorectal cancer [91011].
Several recent studies have suggested that the ratio of preoperative to postoperative serum CEA is an independent predictor of OS for patients with colorectal cancer. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether the perioperative CEA ratio could be used as a determinant for adjuvant therapy after curative surgery on patients with stage II colorectal cancer.
METHODS
A total of 146 patients with stage II colorectal cancer who had undergone radical surgery between 2010 and 2013 at Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital were analyzed retrospectively. TNM pathologic stage II disease was diagnosed according to the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual 7th edition [12]. We excluded patients without records of either preoperative or postoperative serum CEA levels and patients who had previous histories of surgical resection for colorectal cancer. Thus, 119 patients were enrolled in this study. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital and the informed consent was waived.
As a routine practice, we obtain serum CEA levels during the preoperative period and on the seventh postoperative day (median). Quantitative determinations of serum CEA were performed using enzyme immunoassays (ADVIA Centaur Systems, Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Inc., Tarrytown, NY, USA). The normal serum CEA range was defined as below 5 ng/mL. The perioperative CEA ratio was calculated as postoperative/preoperative serum CEA level, and the patients were grouped according to the perioperative CEA ratio: high ratio (≥0.5) and low ratio (<0.5).
Adjuvant chemotherapy was given to all except six patients. A total of 29 patients received intravenous chemotherapy based on 5-fluorouracil. The remaining patients received oral chemotherapy, including 48 patients treated with UFT (tegafur-uracil), 30 patients treated with doxifluridine (5′-deoxy-5-fluorouridine), and 6 patients treated with capecitabine. The expenses for oral chemotherapy are covered by the National Health Insurance Service in Korea; consequently, many patients had received oral chemotherapy. Six of the rectal cancer patients included in the study received preoperative chemoradiotherapy.
The patients were monitored at 3-month intervals for 2 years, at 6-month intervals for the next 3 years, and annually thereafter. History taking, physical examination, and serum CEA assays were performed at each visit. Patients underwent chest computed tomography (CT) and abdominopelvic CT every 6 months, and surveillance colonoscopy was performed a year after surgery and then biannually.
Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 24.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). Survival rates were estimated by using the Kaplan-Meier method, and univariate analyses of the significance of prognostic factors were evaluated by using the log-rank test. A multivariate analysis of factors associated with survival rates was performed using the Cox proportional hazards model with the backward stepwise (likelihood ratio) method. P-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
The clinical characteristics of the patients enrolled in this study are presented in Table 1. The median preoperative serum CEA level, postoperative serum CEA level, and perioperative CEA ratio were 2.52 ng/mL (0.5–530.80 ng/mL), 1.49 ng/mL (0.5–60.73 ng/mL), and 0.5495 (0.02–1.80), respectively. Out of 119 patients, 34 patients (28.6%) had high preoperative CEA levels (≥5 ng/mL) whereas 85 (71.4%) had normal preoperative CEA levels (<5 ng/mL). A total of 66 patients (55.5%) were placed in the high perioperative CEA ratio (≥0.5 ng/mL) group while 53 patients (44.5%) were placed in the low perioperative CEA ratio (<0.5 ng/mL) group. The median age was 71 years (39–86 years), with 63 patients (52.9%) being older than 70.
On the univariate analyses (Table 2), the OS was longer in patients with low perioperative CEA ratios (P = 0.033), age <70 (P = 0.004), and no history of venous invasion (P = 0.012). The patients with better tumor differentiation grades showed a reliable trend (P = 0.092) toward longer survival. The multivariate analysis (Table 3) was performed on the significant factors (P < 0.05) of the univariate analyses. Similarly, age, venous invasion, and perioperative CEA ratio were independent prognostic factors for OS. Fig. 1 depicts the OS curves obtained by using the Kaplan-Meier method and the log-rank test value.
On the univariate analysis, perineural invasion (P = 0.021) was the only significant prognostic factor for disease-free survival (DFS). Patients with low perioperative CEA ratios were not associated with a better DFS rate compared to patients with high perioperative CEA ratios (84.9% vs. 84.8%, P = 0.962). The systemic and the locoregional recurrence rates for the high perioperative CEA ratio group vs. the low CEA perioperative ratio group were 11.3% vs. 13.6% (P = 0.705) and 5.7% vs. 4.5% (P = 0.782).
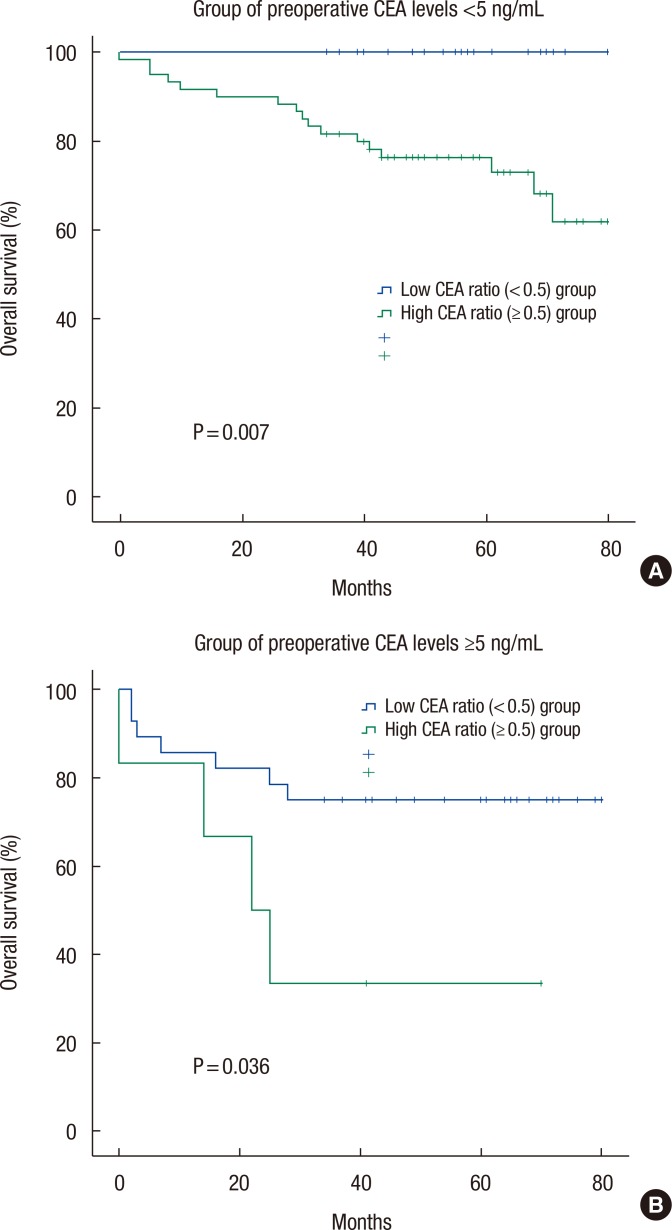
In patients with normal preoperative CEA levels (<5 ng/mL), the OS and the DFS for the high perioperative CEA ratio group (n = 60) vs. the low perioperative CEA ratio group (n = 25) were 71.7% vs. 100.0% (P = 0.007) (Table 4) and 86.7% vs. 88.0% (P = 0.786). In patients with high preoperative CEA levels (≥5 ng/mL), the OS and the DFS for the high perioperative CEA ratio group (n = 6) vs. the low perioperative CEA ratio group (n = 28) were 33.3% vs. 75.0% (P = 0.036) (Table 4) and 66.7% vs. 82.1% (P = 0.184). Fig. 2 depicts the OS curves of the patients based on the perioperative CEA ratio in the groups with normal and high preoperative CEA levels.
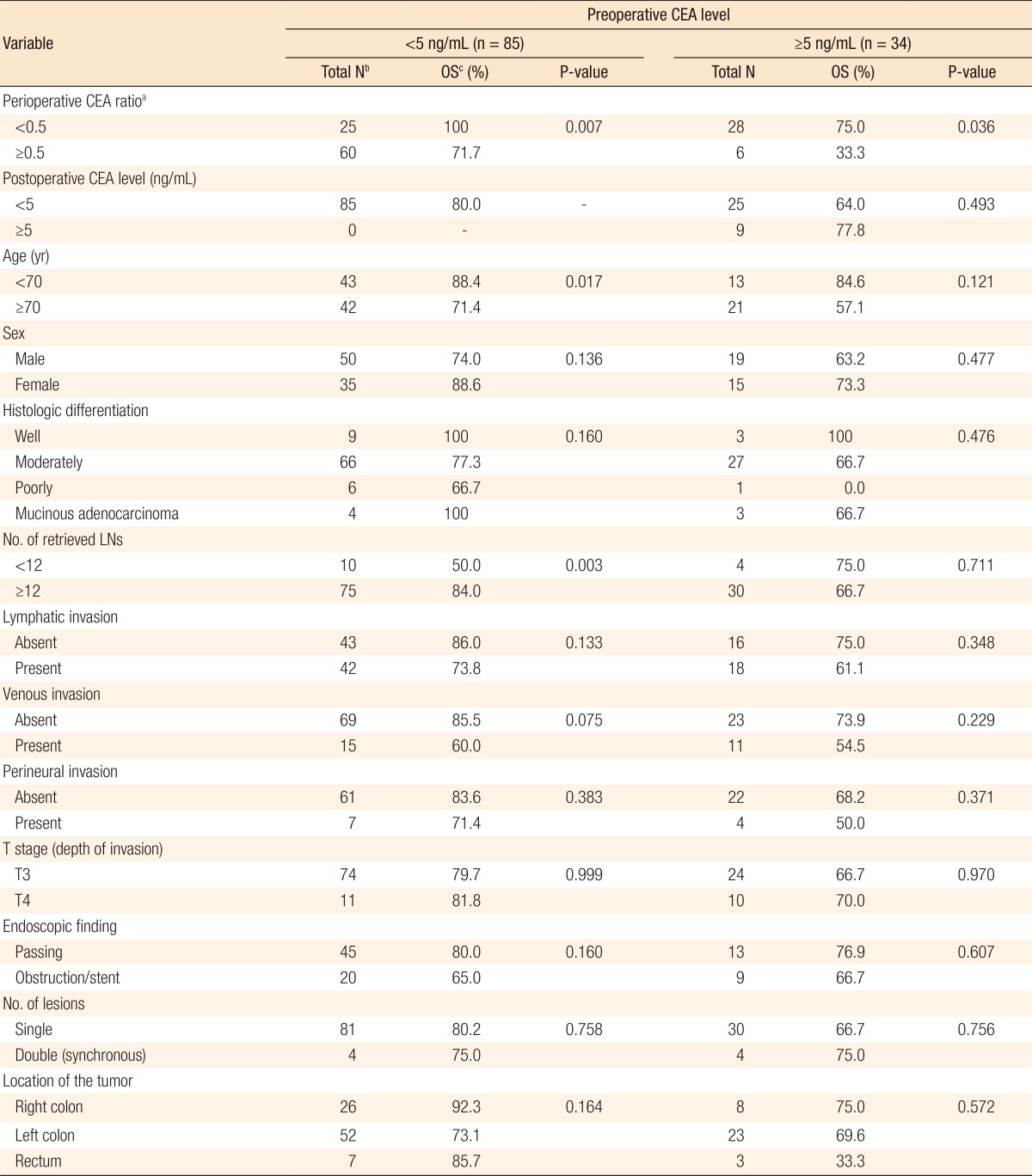
Univariate analyses for independent predictors of overall survival (OS) according to preoperative carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level
DISCUSSION
In stage II colorectal cancer, a survival benefit has not been demonstrated for adjuvant chemotherapy [13]. However, the administration of adjuvant chemotherapy should be considered if high risk factors are present. The ASCO, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, and the European Society for Medical Oncology have suggested several high-risk factors, which include fewer than 12 lymph nodes sampled, poorly differentiated histology, colonic obstruction or perforation, perineural, vascular, or lymphatic invasion, T4 lesions, close or positive margins, and mismatch repair status [714]. Although abundant studies suggest that preoperative CEA is an independent risk factor for survival, no expert panel has accepted elevated preoperative CEA levels as a determinant for adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with stage II colorectal cancer.
In the present study, we observed the following risk factors for patients with stage II colorectal cancer: the presence of lymphatic invasion, age ≥70 years, and high perioperative CEA ratio (≥0.5 ng/mL). However, the preoperative CEA level for OS failed to reach statistical significance, suggesting that a high preoperative CEA level itself lacks the power to discriminate the poor prognostic group in patients with stage II colorectal cancer. Indeed, many researchers have reported results supporting this finding. Moertel et al. [15] stated that CEA was not significantly associated with survival among Dukes' A and B lesions, and other researchers have insisted that the parameter of CEA should reflect postoperative CEA levels [8]. The perioperative CEA ratio we have suggested has strength, in that it covers both preoperative and postoperative CEA levels. The estimated half-life of serum CEA is 3 to 5 days, and if a successful surgical resection is done, high levels of CEA should return to the normal range within 2 weeks to 1 month [1617]. Therefore, the perioperative ratio may reflect how radically the tumor has been resected. Several researchers have suggested that perioperative serum CEA changes in the preoperative and early postoperative periods are predictive of recurrence and prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer [910111819].
The major finding of our study was that the low perioperative CEA ratio (<0.5 ng/mL) group showed better prognosis than the high perioperative CEA ratio (≥0.5 ng/mL) group; that is to say, a decrease in the serum CEA level of over 50% after radical surgery was related to better OS. We have set the reference point for the perioperative CEA ratio as 0.5 ng/mL because previous studies demonstrated that a value close to ‘50% decreased rate’ of perioperative serum CEA had statistical significance in determining OS [1011]. According to these studies, normalization of the early postoperative CEA level and a decreased rate of perioperative CEA could be used as prognostic factors for patients who have elevated preoperative CEA levels [1011]. Similarly, we observed that patients with preoperative CEA levels ≥5 ng/mL had better survival rates if their perioperative CEA ratios were less than 0.5 ng/mL.
An exclusive finding in our study was that the perioperative CEA ratio was associated with survival difference regardless of preoperative serum CEA level. Among the patients with normal preoperative CEA levels, the OS of the low perioperative CEA ratio group was higher than that of the high perioperative CEA ratio group. The conventional view of tumor markers is that when their levels are in the normal range, the risk of recurrence is assumed to be low. However, the CEA level is a marker of considerable individuality, which means that the usual cut-off limits are inappropriate for detecting unusual results in a particular subject [2021]. Instead, serial measurements from an individual form a better basis for early detection of relapse [22]. Therefore, based on our study and those of others, a perioperative change in serum CEA should be calculated even if the preoperative and the postoperative CEA levels are within the normal ranges.
As mentioned previously, the present study suggested the perioperative CEA ratio as an independent prognostic factor for OS. However, in terms of the possible prognostic factors for DFS, the perioperative CEA ratio was not significantly related to the survival rate. In addition, the univariate analysis among the patients with normal preoperative CEA levels (Table 4) proved that a number of retrieved lymph nodes <12, age ≥70 years, and high perioperative CEA ratio (≥0.5 ng/mL) were poor prognostic factors. However, when a multivariate analysis was performed, age ≥ 70 years (P = 0.018; hazard ratio, 3.425; 95% confidence interval, 1.235–9.501) was the only significant factor whereas the number of retrieved lymph nodes (P = 0.084) and the perioperative CEA ratio (P = 0.959) lost their significance. This may limit the validity of the conclusions of the present study. In both groups, normal and high preoperative CEA levels, patients with T4 stage showed better survival rate than patients with T3 stage (Table 4). The small number of samples might be cause of the outcome, which is different from general expectation. Further research on a large population of patients is necessary to investigate the perioperative CEA ratio and prognostic factors.
In conclusion, the perioperative CEA ratio is a prognostic indicator for patients with stage II colorectal cancer. Our study confirmed that the perioperative CEA ratio could be a better prognostic factor than the preoperative and the postoperative CEA levels. Patients with normal preoperative serum CEA levels should also be monitored thoroughly and considered for adjuvant therapy if their perioperative CEA ratios are higher than 0.5 ng/mL.
Notes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.